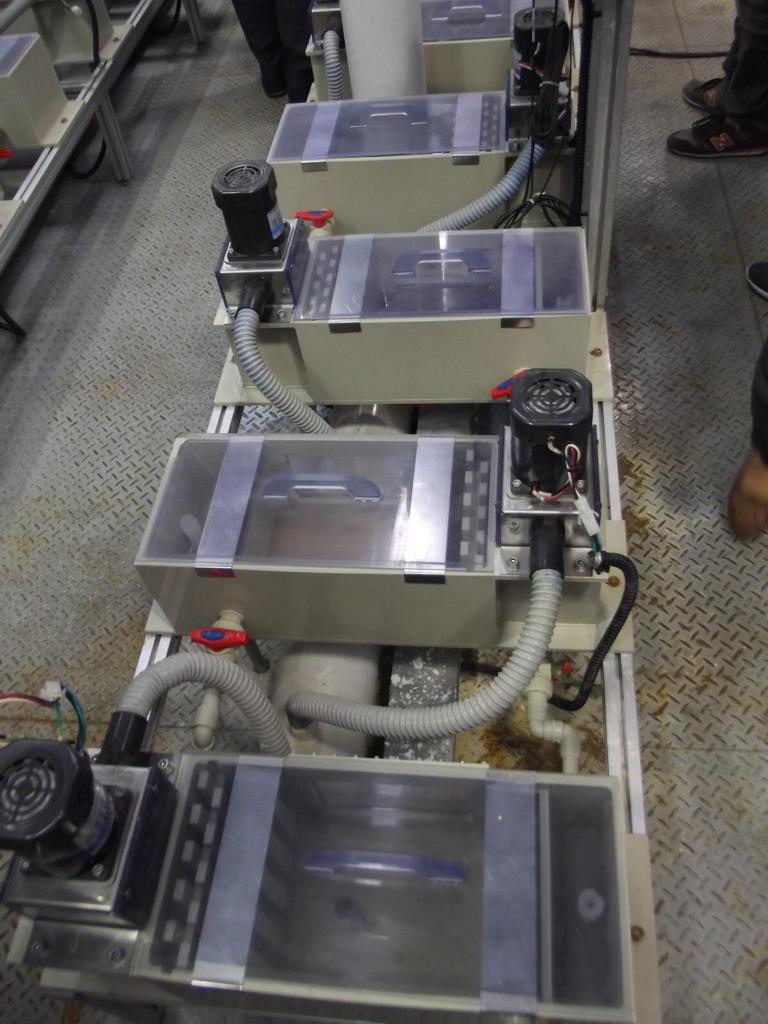
Solvent extraction is the transition of one or more compounds from one phase to another as a result of the contact of two insoluble or partially dissolved liquid phases.
Solvent extraction process is to ensure that the metal ion present at low concentrations in an aqueous solution or the desired ion from different metal ions present in complex aqueous solutions forms a temporary bond with a liquid organic compound that is insoluble in the aqueous solution, depending on the solution pH, and to recombine the metal ions enriched in the organic phase. It consists of the steps of taking it into aqueous solution. These two basic steps are called “Loading” and “Stripping”.[1]